The debate over the logic of occupying Siachen glacier is not new. But the recent death of 10 Indian soldiers is a reason to remind ourselves why it continues to be a painful necessity.
Few individual military stories have galvanized India as the heroic battle fought by Lance Naik Hanumanthappa and his comrades against terrifying odds at Siachen recently. Their story has once again focused attention on what has long been a “forgotten war” in our public consciousness. But few really understand why Indian soldiers fight and continue to die in the world’s most unforgiving battlefield.
A trekker and ‘oropolitics’
It all started with a German tourist and an American map. For the first three decades after Independence, even Pakistani maps didn’t show Siachen on their side of Kashmir’s Line of Control (LoC). But when several international publishers like National Geographic’s Atlas of the World suddenly started doing so in the 1970s, alarm bells began to ring in the Indian Army. Pakistan had been issuing permits for mountaineering expeditions in the Siachen glacier but when the boss of the Indian Army’s mountain warfare school, Colonel Narendra Kumar, met a German mountaineer with an American map showing a large chunk of the eastern Karakoram, including the Siachen glacier, as having ceded to Pakistan he immediately bought it and send it to the Director General of Military Operations with a request for an expedition to “correct the map”.
Kumar’s 1978 military expedition to Siachen, with Pakistani Army helicopters buzzing overhead when they reached, was the beginning of what came to be called “oropolitics” — mountaineering with a political goal — and a new dynamic in the India-Pakistan equation. At stake was the alignment of the LoC north of where it abruptly terminated at NJ 9842 in the 1949 ceasefire agreement (it was left undefined in these parts as no one lived there). Pakistan insisted that the LoC went northwards from there, putting the Siachen glacier in its territory; India, though, argued that the LoC must follow the geographical features of the Saltoro ridge, thus putting Siachen in its operational half.
With Pakistan looking to stake its claim, the Indian Army answered with its Operation Meghdoot on April 13, 1984, after military intelligence learnt of Pakistan shopping for high-altitude equipment in London. Indian troops beat the Pakistanis to Siachen by a week and have controlled it ever since.
Two bald men fighting over a comb?
The Indian Army has long been opposed to demilitarizing Siachen, and Pakistan has been pressing for it, essentially because India holds the formidable Saltoro ridge. Indian troops control the major passes — Turkistan La (connecting Shaksgam Valley which Pakistan ceded to China in 1963), Indra col, Sia La, Bilafond La and their positions completely dominate Pakistani deployments on the lower western slopes.
Does this tactical advantage translate into long-term strategic gain? Lt Gen ML Chibber, Northern Army Commander at the time of India’s occupation of Siachen, explained in 1990 that the original occupation was meant “only to deter the Pakistanis from getting there first. The Indian Army had no plans for permanent occupation”. At the end of the day, he argued, “the Siachen conflict was a mistake”.
Several other former military officers have echoed this sentiment. In an important 2007 paper, the military analyst, Brigadier Gurmeet Kanwal (retd.), for example, emphasized that Siachen has “very little military significance”. Similarly, the strategic affairs analyst Stephen Cohen, who has closely studied both the Indian and Pakistani armies, once famously called the Siachen conflict a case of “two bald men fighting for a comb”.
The Indian Army though has vehemently argued in favour of Siachen’s importance. In the UPA years, when Prime Minister Manmohan Singh called Siachen a “mountain of peace”, then Army chief General Bikram Singh publicly argued against proposals for demilitarization. The argument is that Siachen could be a base for northwards operations along the Karokaram highway, if required, and that it is critical for guarding against troop movements by China and Pakistan across Baltistan, Aksai Chin and Shaksgam Valley. It is also important for monitoring the Nubra and Shyok valleys.
Fighting ‘General Glacier’
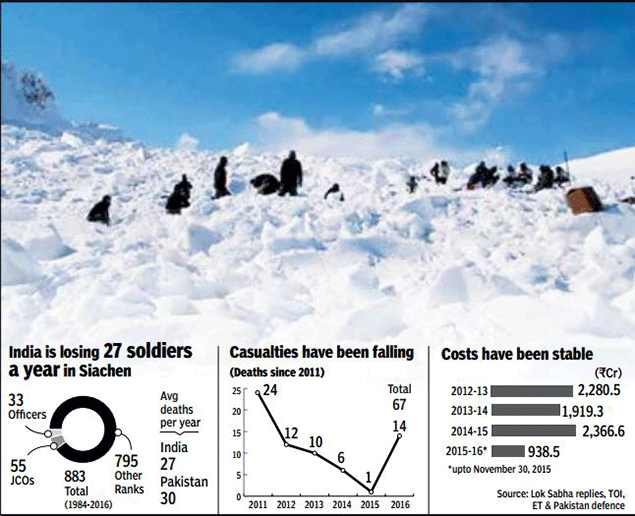
There is no doubt that the biggest problem is fighting “General Glacier”, not the enemy. MoD data shows that India has lost almost 900 soldiers since 1984 — mostly to natural calamities and illnesses caused by oxygen deprivation and temperatures dipping to -50 degrees Celsius.
While the army’s average yearly death count has significantly reduced in the last five years due to better equipment and technology and is much better than Pakistan’s annual casualty average, almost all Indian casualties in recent years accrue to the weather or health conditions (see charts). The casualty figures also do not reflect the hidden cost of Siachen — many soldiers come back with life-long problems of memory loss, blood clots in vital organs and other life-threatening issues. There is, for example, the case of Lt Col Rajesh Mehta, documented by the journalist Nitin Gokhale. The officer suffered such serious blood clotting in his limbs that three of them had to be amputated.
Army troops in Siachen are rotated every three months but to be deployed in a place where simply being around can be life-threatening is a Herculean task indeed.
Demilitarization?
Talk on demilitarization in the past has fallen through because of Pakistan’s refusal to validate actual ground positions on the glacier. At a disadvantage in Siachen, Pakistan has long been a votary of demilitarization but the fear is that a withdrawal without guarantees could simply allow Pakistan to walk into vacated posts. It is often forgotten that the Kargil War was justified by General Musharraf as a means of cutting Indian troops in Siachen and as a response to what Pakistan sees as Indian aggression there.
After the Pakistani Army suffered heavy losses in the Gayari sector in 2012, its then chief General Kiyani again called for vacating Siachen. Yet, at a time when Siachen is a symbol of muscular nationalism and emotive territorialism, it is difficult to reach even for low-lying fruits in the India-Pakistan face-off. Meanwhile, soldiers continue to die.
The other side of the story
The Gayari tragedy in 2012 led to an emotive public debate in Pakistan’s media on the human costs of the Siachen standoff. Then army chief General Ashfaq Pervez Kiyani called for the demilitarization of Siachen, a position that Pakistan, at a military disadvantage in the glacier, has long supported. In 2015, a play called ‘Siachen’ by Anwar Maqsood debuted before packed audiences. Its script was approved by Pakistan’s Inter-Services Public Relations (ISPR). Pakistan’s high commissioner to India Abdul Basit also repeated the call for a mutual withdrawal of troops on February 11, 2016. India’s response, enunciated by Lt General DS Hooda, GOC-in-C, Northern Command is clear: “If we have to talk about the withdrawal (of troops from Siachen), first the actual positions on the ground, where we are today and where our posts are, need to be authenticated.”